Breast Implant Placements
Breast Implants Over or Under or Breast Implants above and below the muscle are the traditional options that come to mind when you consider your breast implant placement. But it is a lot more technical than that and there is usually a variety of different options for you to choose from.
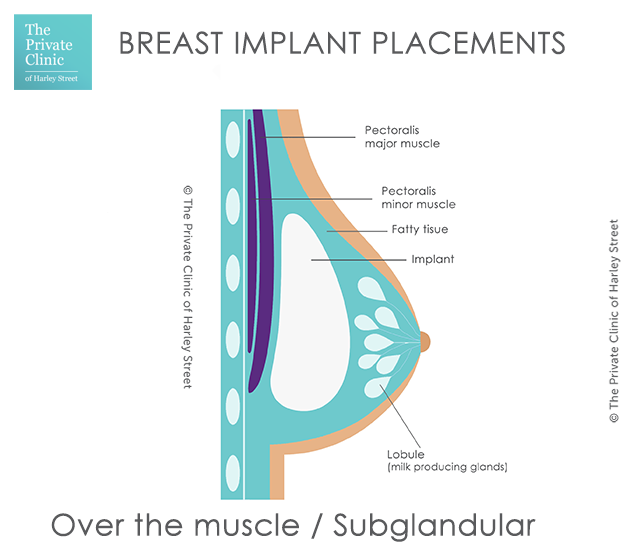
What is Subglandular implant placement?
Over, Above the muscle or Subglandular as it may be referred to by your plastic surgeon is when your breast implants are placed over the chest or pectoral muscles.
What are the pros and cons of over the muscle implants?
| Pros | Cons |
| Shorter recovery time | Not ideal for women with minimal breast tissue |
| Easier surgical procedure | Not ideal for saline implants |
| Less discomfort post-op | May give a ‘fake’ appearance if breast tissue is minimal |
| Good for women with a moderate amount of breast tissue. | Visible ripping may occur over time |
| Implant distortion risk decreased |
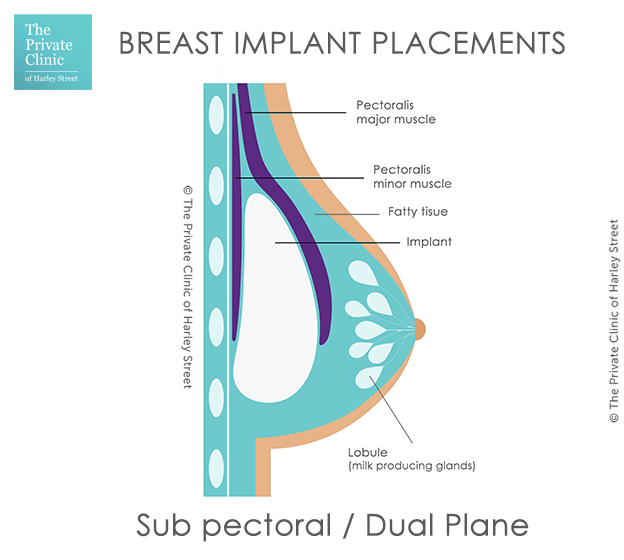
What is Dual Plane implant placement?
Dual plane is usually classed as ‘under’ or below however the implant does not sit completely under the muscle. The upper portion of the implant is placed under the pectoral muscle, but the lower portion is left uncovered. Dual plane may also be known as partial submuscular, sub pectoral and the split muscle / split pectoral muscle technique.
What are the pros and cons of Dual Plane implants?
| Pros | Cons |
| Can improve breast asymmetry | More complicated surgical procedure |
| Can lift the breast slightly | More discomfort may be felt during recovery |
| More natural result | Implants may be prone to distortion when the chest muscle contracts |
| Reduced risk of implant sagging | Temporary loss in chest muscle strength post-op |
| Easier to have a mammogram | |
| Less risk of implant rippling | |
| Reduced risk of capsular contracture |
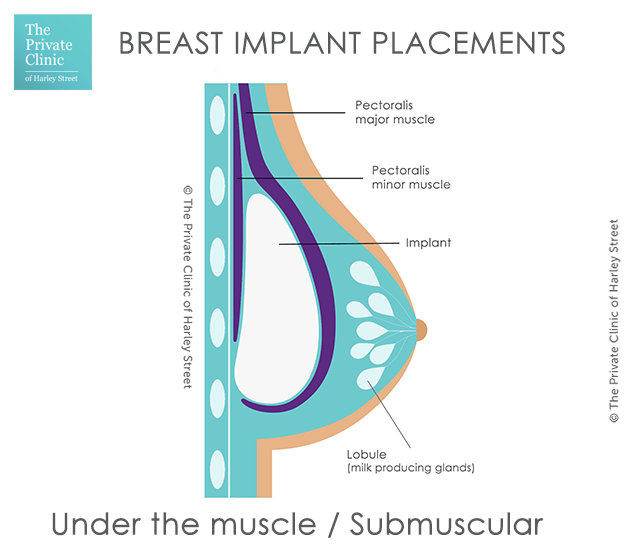
What is Under the muscle implant placement?
Under or Submuscular is when the breast implant is placed below the pectoralis muscle. It is not commonly performed and usually when surgeons refer to ‘under the muscle’ they actually mean ‘dual plane’ or ‘split muscle’.
What are the pros and cons of submuscular implants?
| Pros | Cons |
| Less risk of implant rippling | Implants may feel tight |
| Implants can sit high on the chest | |
| Implants may change shape with arm and chest muscle movement | |
| Patients can feel chronic pain or discomfort | |
| Longer recovery time | |
| Complicated surgical procedure |
What is Subfascial implant placement?
Subfascial implant placement is also not that commonly performed. It involves placing the breast implant beneath a thin layer of fascia which is connective tissue that covers the pectoral muscle. This can be quite a difficult procedure as the fascia is very thin and it can be tricky to cover the entire implant.
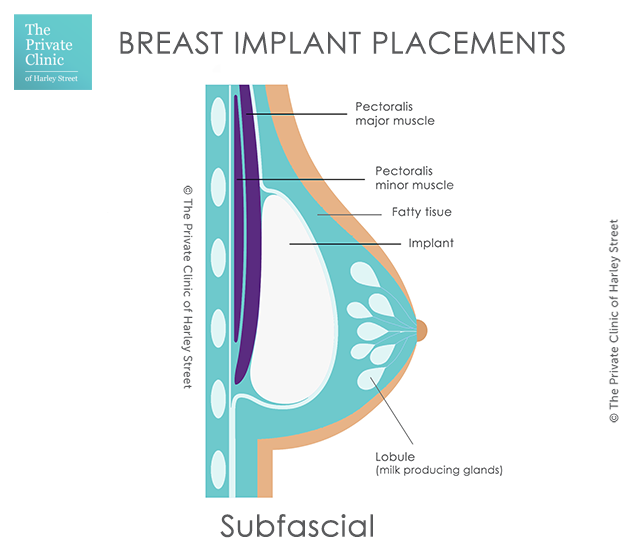
What are the pros and cons of subfascial implant placement?
| Pros | Cons |
| Reduced risk of capsular contracture | Difficult procedure |
| Reduced risk of rippling | May experience increased bleeding |
| More natural-looking results | Long-term comparative studies still not available |
| Patients feel less discomfort post-op | Potential trauma whilst separating the fascia tissue |
What is the most common breast implant placement?
The dual plane is the most common breast implant placement. There are also a few different variations to the dual plane technique which usually varies the amount of coverage that the muscle has over the implant.
How do I know which implant placement is the best for me?
Knowing what implant placement is best for you is a difficult task. Our surgeons are very experienced in offering their advice on implant placement, which is usually based on your breast measurements, amount of natural tissue, size of desired implants and lifestyle impacts. All of our surgeons at The Private Clinic have your best interests at heart and will be able to help you to make an informed decision on the placement of your implants.
Our Expert Breast Surgeons
- Mr Davood Fallahdar, MD&Surg (Hons), FRCS (Eng), Chir Plast (Hons), MicroSurg (Hons), ORL (H&N) GMC Number: 4686602
- Mr Dario Rochira, BS, MD. GMC Number: 6130664
- Ms Helena Antoniadou, MBBS, MD & Surg (Hons), FRCS (Eng). GMC Number: 3700956
- Mr Maisam Fazel, MA(Cantab), MB BChir, MSEd, FRCS. GMC Number : 4767420
- Mr Giuseppe Di Taranto, MD. GMC Number: 7614248
- Professor Sandip Hindocha, MD, MPhil, MBChB, MRCS, MFFLM, FRCS (Plast). GMC Number: 6122218
- Ms Rieka Taghizadeh, MBChb, MRCS (Glas), FRCS (Plast), GMC Number: 4743910
- Mr George Samouris, MD. GMC Number: 7064009
Why choose The Private Clinic for Breast Implant Surgery?
- The Private Clinic has been treating patients for over 40 years with thousands of women placing their trust in us each year.
- Top UK specialised best breast surgeons with decades of experience.
- State-of-the-art hospital facilities
- Giving you the best possible results and care is our priority.
- Dedicated care with your expert breast surgeon and nursing team, and a 24-hour helpline
- 5 Star Trustpilot Rating
- All of the breast options are discussed not just one type of implant. So you will be happy with your shape
Helpful links
- See our before and after photo results gallery
- Read our extensive FAQs
- Find out more in our informative blogs
- We have clinics in London Harley Street, Birmingham, and Northampton
Get in touch
To find out more about Breast Enlargement Surgery, please call us on 0333 920 2471 or use our online breast implant contact form.







